
Once a request has been made, the user on the local client must input the unattended access password to connect.

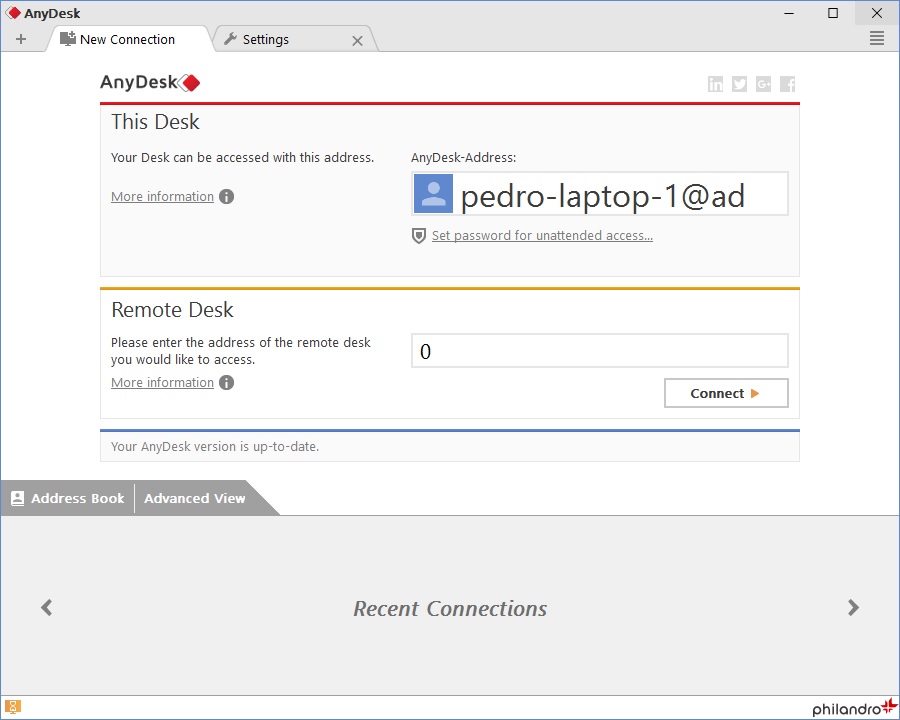
On the flip side, one can also be sent by clicking the client tiles located in Discovery, Favorites, Recent sessions, and the Address Book. You can also utilize this address from another PC to remote desktop into your Fedora PC. You can send a connection request to a remote client by inputting the AnyDesk-ID in the “Remote Desk” field. The first element we will look at is the address of your AnyDesk client. With it up and running, let us take you through some critical elements you must be aware of. You should, at this point, have AnyDesk opened on your Fedora system. This section will display how to open the software and take you through a dry run of its basic features. Now that we have AnyDesk installed on our Fedora system, we are sure you are itching to know how to use it. Launch AnyDesk via GUI How to use AnyDesk on Fedora To begin, sign in as root in your Fedora system by running the following command: Yum and dnf are basically primary package management tools for setting up, updating, deleting, and managing software packages in Red Hat Enterprise Linux, like Fedora. We will also use the Yum and dnf package managers. In this article, we will use Fedora version 37, which is the latest at the time of this writing.
Let’s get the article underway! Method 1: Installing AnyDesk on Fedora An SSH access to the server (or open the terminal if you’re using the desktop).But before we start, here are some of the requirements. Here is the step-by-step procedure for getting this software up and running on your Fedora system. The installation is simple, and we think you are running in the root account if not, you may have to append “sudo” to the command to get root privileges.

This guide assumes you at least have some clue of basic Linux knowledge, like knowing how to use the shell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
